Keeping your network safe from intrusion is one of the most vital parts of system and network administration and security. If your network is penetrated by a malicious attacker, it can lead to massive losses for your company, including potential downtime, data breaches, and loss of customer trust.
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a tool or software that works with your network to keep it secure and flag when somebody is trying to break into your system. There are several different types of IDS and numerous tools on the market and figuring out which one to use can be daunting.
In this ultimate guide, I’ll go through everything you need to know (and I mean EVERYTHING) about IDS: what an intrusion detection system is, how network intrusion works, how to detect network intrusion, as well as which tools you should consider with my reviews of the latest IDS software – including my favorite pick SolarWinds® Security Event Manager.
How Does Network Intrusion Work?
Scanning Attacks
Asymmetric Routing
Buffer Overflow Attacks
Protocol-Specific Attacks
Malware
Traffic Flooding
What Is an Intrusion Detection System?
Types of Intrusion Detection System
What Is a Network Intrusion Detection System?
What Is a Network Node Intrusion Detection System?
What Is a Host Intrusion Detection System?
Signature-Based IDS
Anomaly-Based IDS
IDS vs. Intrusion Prevention Systems vs. Firewalls
Security Information and Event Management
IDS for Windows
IDS for Mac
IDS for Linux
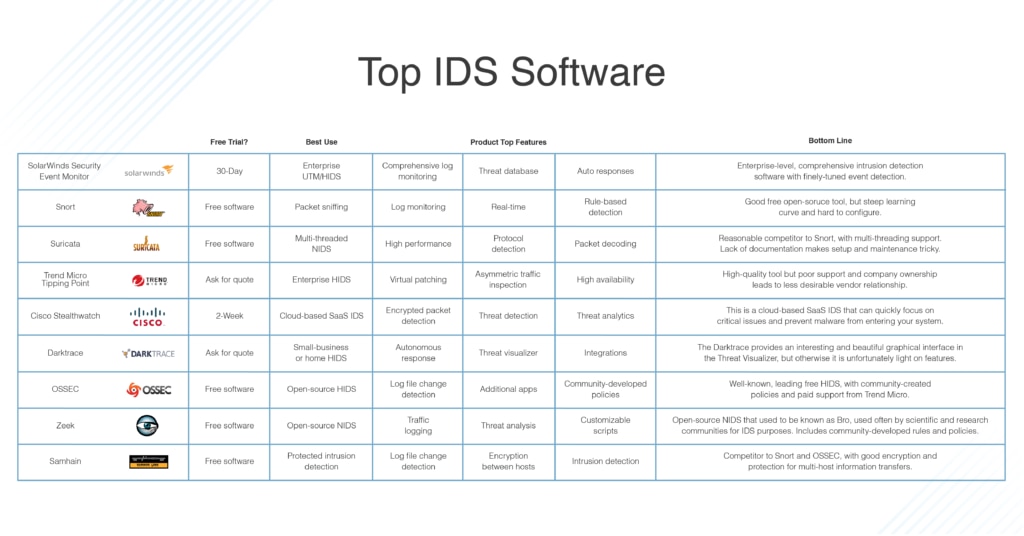
SolarWinds Security Event Manager
Snort
Suricata
Trend Micro TippingPoint
Cisco Stealthwatch
Darktrace Enterprise Immune System
OSSEC
Zeek
Samhain
IDS Configuration and Use Best Practices
Final Thoughts on Using an IDS System
How Does Network Intrusion Work?
Attackers can take several different approaches when attempting to penetrate a system. With network intruder detection software, understanding what kinds of attacks can be used is critically important for setting up effective prevention. I’ll go through some of the most common types of network intrusion and attack, so you have a clear understanding of what a network intrusion detection system tries to prevent.
In many cases of network intrusion, the attack involves flooding or overloading the network, gathering data about the network to attack it from a weak point later, or inserting information into the network to spread and gain access from inside. It’s important to keep hacker detection tools active, so you can prevent these vulnerabilities from getting into your system in the first place.
Scanning Attacks
One kind of attack is a scanning attack, which involves sending packets or information to the network, attempting to gather data about the network topology, open or closed ports, types of permitted traffic, active hosts on a network, or what types or versions of the software are running. Blind SQL injection attacks can use some of these scanning techniques as they attempt to find more vulnerable points in the network. Scanning attacks often look for open ports where viruses or malicious code can be inserted.
Asymmetric Routing
Asymmetric routing is when packets traveling through the network take one route to their destination, then a different route back. This is normal but unwanted network behavior. Depending on how your firewalls are set up, attackers can use asymmetric routing behaviors to send malicious packets through certain parts of your system to bypass your security setups. Generally, allowing your network to perform asymmetric routing can leave you open to SYN flood attacks (a type of DDoS attack), and in most cases should be turned off for better network protection.
Buffer Overflow Attacks
This kind of attack attempts to penetrate sections of memory in devices on the network, replacing normal data in those memory locations with malicious data to will be executed later in an attack. In most cases this is also intended to turn into a form of DDoS attack. Basically, a buffer section of memory can contain a character string or a large array of integers. A buffer overflow is when more data is written to the buffer than it can handle, which results in data overflowing into adjacent memory. This can cause the entire system to crash and can also create confusion and problems, hiding an attack in another part of the system.
Protocol-Specific Attacks
These kinds of attacks target specific protocols, including ICMP, TCP, and ARP.
ICMP stands for Internet Control Message Protocol and is used by network devices to communicate with each other. The ping and traceroute tools use ICMP to communicate. One kind of ICMP attacks are also known as ping floods, in which the attacker overwhelms a device with ICMP echo-request packets. This works because the ICMP requests require bandwidth to work, and an attack increases this network load substantially. While the device is busy dealing with this large number of malicious packets, it can’t handle normal requests. The ICMP protocol can also be used in ICMP tunneling attacks, where data is sent through ICMP packets (which can bypass firewalls), smurf attacks, (where the address the packet is coming from is spoofed), and port scanning, where ICMP error messages are used to detect whether specified ports are open.
TCP can also be used for specific kinds of attacks, such as the TCP SYN flood. Transmission Control Protocol normally works with a “three-way handshake” to connect two devices. First, the client requests a connection by sending a synchronize (SYN) message to the server, which the server acknowledges by sending a synchronize-acknowledge (SYN-ACK) message back. Finally, the client responds with an acknowledge (ACK) message, and the connection will be complete. A TCP SYN flood is when an attacker sends a large number of SYN messages to different ports on the targeted server, but never sends the ACK message. As a result, the ports stay open while they wait for the ACK message to be received, during which time the attacker sends more SYN messages, the server’s connection overflow tables fill, and the system will crash or malfunction.
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol, and can also be used in flooding attacks, by sending large numbers of ARP packets to a recipient to overflow their ARP tables, like the above attacks. Forged or spoofed ARP packets can also be sent. ARP poisoning is where the attacker sends false ARP messages to link the attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate network device. Once the attacker has a valid link to this legitimate IP address, the attacker can intercept messages directed to the legitimate MAC address and modify or stop those messages.
Malware
There are several different kinds of malware, including worms, trojans, viruses, and bots. Malware is a type of software designed to damage or disrupt your system. Malware is often accidentally downloaded via email or included with another software package. Others get into your system by exploiting weaknesses in browsers, software, your network, or network devices.
Some of the most well-known types of malware are viruses and worms. These types of malware can self-replicate and spread quickly throughout your system. Worms can self-propagate, while viruses use host programs to replicate and spread.
Viruses are generally attached to .exe files, and the virus isn’t necessarily active until the user runs the malicious .exe program. As soon as the user runs this program, the virus will run as well. As they spread, viruses infect one device after another. Worms are standalone software and don’t need host programs to continue to spread. In many cases, they’ll exploit a software loophole or trick users into running them.
A trojan software disguises itself as a normal program, such as a document that looks legitimate but is malware. Unlike worms and viruses, they don’t self-replicate and can only be spread by other users.
Bots will infect a device and then connect back to a central control server. The central control server can then use all the devices infected with bots as a “botnet” to launch high-powered attacks on other targets.
Traffic Flooding
In many cases, this is a type of attack called a DDoS attack, or Distributed Denial of Service attack. Some of the above attacks, including buffer overflow attacks and asymmetric routing attacks, use traffic flooding.
What Is an Intrusion Detection System?
When I think of what a good intrusion detection system would be, I think of a system intended to discover threats before they fully enter the system.
Intrusion detection systems are usually a part of other security systems or software, together with intended to protect information systems. IDS security works in combination with authentication and authorization access control measures, as a double line of defense against intrusion. Firewalls and antivirus or malware software are generally set up on each individual device in a network, but as enterprises grow larger, more unknown or new devices come in and out, such as cell phones and USBs. Firewalls and anti-malware software alone is not enough to protect an entire network from attack. They act as one small part of an entire security system.
Using a fully-fledged IDS as part of your security system is vital and is intended to apply across your entire network in different ways. An IDS can capture snapshots of your entire system, and then use the intelligence gathered from pre-established patterns to determine when an attack is occurring or provide information and analysis on how an attack occurred.
Essentially, there are several components to intrusion preparation: knowledge of potential intrusions, preventing potential intrusions, being aware of active and past intrusions, and responding to the intrusion. While it may seem “too late” once an attack has already happened, knowing what intrusions have happened or have been attempted in the past can be a vital tool in preventing future attacks. Knowing the extent of the intrusion of an attack is also important for determining your response and responsibilities to stakeholders who depend on the security of your systems.
Types of Intrusion Detection System
You might be wondering: what are the different ways to classify an IDS? There are three main types of intrusion detection software, or three main “parts,” depending on if you view these all as part of one system:
- Network Intrusion Detection System
- Network Node Intrusion Detection System
- Host Intrusion Detection System
At the most basic level, Network Intrusion Detection Systems and Network Node Intrusion Detection Systems look at network traffic, while Host Intrusion Detection Systems look at actions and files on the host devices.
What Is a Network Intrusion Detection System?
A Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) is generally deployed or placed at strategic points throughout the network, intended to cover those places where traffic is most likely to be vulnerable to attack. Generally, it’s applied to entire subnets, and it attempts to match any traffic passing by to a library of known attacks. It passively looks at network traffic coming through the points on the network on which it’s deployed. They can be relatively easy to secure and can be made difficult for intruders to detect. This means an intruder may not realize their potential attack is being detected by the NIDS.
Network-based intrusion detection system software analyzes a large amount of network traffic, which means they sometimes have low specificity. This means sometimes they might miss an attack or might not detect something happening in encrypted traffic. In some cases, they might need more manual involvement from an administrator to ensure they’re configured correctly.
What Is a Network Node Intrusion Detection System?
A Network Node Intrusion Detection System (NNIDS) is like a NIDS, but it’s only applied to one host at a time, not an entire subnet.
What Is a Host Intrusion Detection System?
The Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) runs on all the devices in the network with access to the internet and other parts of the enterprise network. HIDS have some advantages over NIDS, due to their ability to look more closely at internal traffic, as well as working as a second line of defense against malicious packets a NIDS has failed to detect.
It looks at the entire system’s file set and compares it to its previous “snapshots” of the file set. It then looks at whether there are significant differences outside normal business use and alerts the administrator as to whether there are any missing or significantly altered files or settings. It primarily uses host-based actions such as application use and files, file access across the system, and kernel logs.
Network and host-based intrusion detection systems are the most common ways of expressing this classification, and you won’t find NNIDS mentioned very often in this space. Just think of it as a type of NIDS.
There are also two main approaches to detecting intrusion: signature-based IDS and anomaly-based IDS.
Signature-Based IDS
This type of IDS is focused on searching for a “signature,” patterns, or a known identity, of an intrusion or specific intrusion event. Most IDS are of this type. It needs regular updates of what signatures or identities are common at the moment to ensure its database of intruders is current. This means signature-based IDS is only as good as how up to date its database is at a given moment.
Attackers can get around signature-based IDS by frequently changing small things about how the attack takes place, so the databases cannot keep pace. In addition, it means a completely new attack type may not be picked up at all by signature-based IDS because the signature doesn’t exist in the database. Furthermore, the larger the database becomes, the higher the processing load is for the system to analyze each connection and check it against the database.
Anomaly-Based IDS
In contrast to signature-based IDS, anomaly-based IDS looks for the kinds of unknown attacks signature-based IDS finds hard to detect. Due to the rapid growth in malware and attack types, anomaly-based IDS uses machine learning approaches to compare models of trustworthy behavior with new behavior. As a result, strange- or unusual-looking anomalies or behavior will be flagged. However, previously unknown, but legitimate, behavior can be accidentally flagged as well and depending on the response, this can cause some problems.
In addition, anomaly-based IDS assumes network behavior always stays predictable and it can be simple to tell good traffic from bad. But anomaly-based IDS looks at the behavior of traffic, not the payload, and if a network is running on a non-standard configuration, the IDS can have problems figuring out which traffic to flag.
However, anomaly-based IDS is good for determining when someone is probing or sweeping a network prior to the attack taking place. Even these sweeps or probes create signals in the network the anomaly-based IDS will pick up on. This type of IDS needs to be more distributed across the network, and the machine learning processes need to be guided and trained by an administrator.
IDS vs. Intrusion Prevention Systems vs. Firewalls
An IDS is an intrusion detection system, not a system designed to respond to an attack. An IDS can be part of a larger security tool with responses and remedies, but the IDS itself is simply a monitoring system.
Another kind of system is the Intrusion Prevention System or IPS. An IPS is essentially an IDS combined with a response or control system. IDS doesn’t alter network packets as they come through, while the IPS will prevent the packet from being delivered based on the contents of the packet (e.g., if it sees the packet is malicious).
Both a (signature-based) IDS and IPS refer to a database of known threats, and then flag or respond to the threat based on this database. IDS requires an administrator to look at the results of what has been flagged, whereas an IPS will take action automatically to block the threat. In most ways, both IDS and IPS are largely hands-off, and even an IDS will simply send alerts to the administrator for them to respond to (the admin doesn’t have to review every single IDS process themselves). As a result, these can be useful and low-maintenance tools in your security stack.
You may also be wondering what the difference is between an IDS and a firewall. Generally, a firewall is supposed to be configured to block all traffic, and then you set it up to allow specific types through. The IDS and IPS work in the opposite direction, by allowing all traffic and then flagging or blocking specific traffic only. As a result, you should use a firewall in combination with an IDS or IPS, not one or the other. Set up your firewall to let only specific kinds of traffic through, and then use the IDS to detect anomalies or problems in the traffic you permit. The combination of these tools provides a comprehensive security boundary for your network.
An IPS may appear more useful than an IDS simply because it “does more,” but passive listening to network behavior is still vitally important. A lot of traffic looks suspicious but is, in fact, innocent, and if your tool is always automatically blocking or reacting to traffic, you can end up with false positives interfering with normal network traffic. In either case, you need to configure your IDS or IPS to minimize false positives and negatives and to ensure accuracy as frequently as possible.
Security Information and Event Management
When you are looking into which IDS to use, you might see the term “Security Information and Event Management,” or SIEM. SIEM is a combination of Security Information Management (SIM) and Security Event Management (SEM). Basically, SEM is a kind of SIEM that looks at network traffic, like a NIDS does. These two areas overlap, and in some cases to find a good IDS tool, you’ll also need to look at tools classified as SEM software.
Choosing IDS Software
If you’re trying to decide between a host-based or network-based IDS, remember they both serve different purposes and in most cases, you’ll need both systems simultaneously, or a tool to provide both. The host-based intrusion detection system can detect internal changes (e.g., such as a virus accidentally downloaded by an employee and spreading inside your system), while a network-based IDS will detect malicious packets as they enter your network or unusual behavior on your network such as flooding attacks or protocol-specific attacks.
Remember there are also different people in your organization who should be involved in choosing and deploying your IDS system. They include:
- Management
- Information security officers
- Employees who “own” or look after sensitive data
- Network admins
- Database admins
- SysAdmins
All these people will have a good idea of network vulnerabilities and can contribute to deciding where IDS should be deployed about your network, and what kind of behavior it should be configured to detect. If you don’t involve these critical people in choosing and setting up your IDS, you could end up missing important vulnerabilities or sensitive information in need of extra protection. The best approach is to hold a vulnerability and risk assessment meeting before you deploy and set up your IDS.
In any case, if you don’t already have an IDS set up for your business, make sure you get the process started as soon as possible. These detection systems are vital for security and shouldn’t be overlooked.
Latest and Top IDS Software
You can choose from several different IDS tools, depending on which operating system you’re using. So, I split my recommendations up by OS to help you focus on the solutions compatible with your environment.
All the different systems in my top IDS software list also have free trials, so you can try a few of them out and see which one you like the best. If your organization works with any data requiring particular security measures, such as HIPAA data or PCI data, you’ll need an IDS system in place to meet your compliance and audit obligations.
IDS for Windows
IDS for Mac
IDS for Linux
1. SolarWinds Security Event Manager
SolarWinds Security Event Manager (SEM) is an intrusion detection system designed for use on Windows Server. It can, however, log messages generated by Windows PCs and Mac OS, as well as Linux and Unix computers.
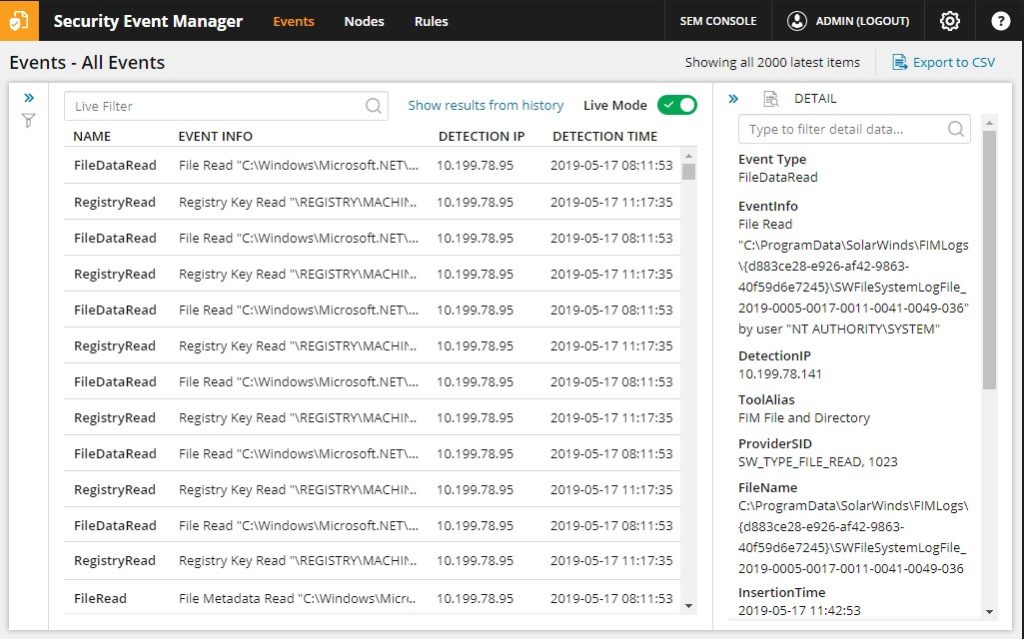
This is primarily a host-based intrusion detection system and works as a log manager. It examines connected USB devices and files coming in and out of the network and checks them for integrity and malicious modifications. It also regularly checks the filesystem itself to ensure files have not been modified, deleted, or moved in unusual ways.
SEM also can link in with and manage data collected by Snort, turning it into a more comprehensive threat-detection system with network-based intrusion detection. To use these capabilities, you need to use Snort as a packet capture tool, and then funnel this captured data to SEM. SEM can then analyze this data and detect intrusions through the network.
The tool includes knowledge-gathering processes to find relevant and up-to-date information on known botnets and other malicious actors to detect bots or intruders. This means you can configure automatic responses to known intruders, without needing to use custom scripts.
Finally, SEM can act as an intrusion prevention system as well, since it can react actively to intrusion events.
SEM can use active responses, including:
- Alerts via SNMP, screen messages, or email
- USB device isolation
- User account suspension or user expulsion
- IP address blocking
- Processes killing
- System shutdown or restart
- Service shutdown
- Service triggering
The multi-faceted approach of SEM makes it a comprehensive and robust tool able to take care of most incident detection, prevention, and security analysis needs. It’s well-equipped enough to work at an enterprise level and is high-quality software that I highly recommend. You can try out a free trial for up to 30 days.
2. Snort
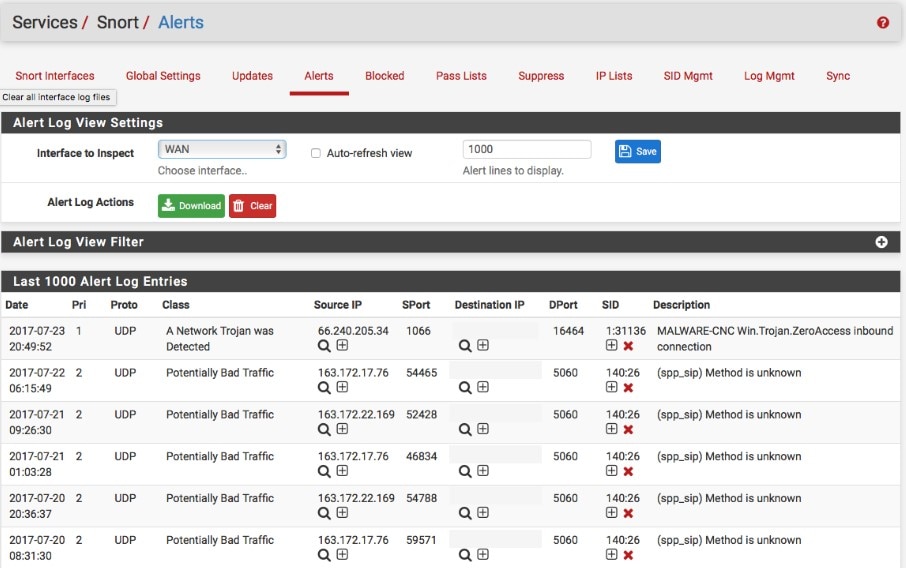
Snort is a well-known and currently industry-leading tool used for packet sniffing, logging, and intrusion detection. It was created by Cisco and can be installed on Windows as well as a few Linux distributions.
The combination of its three different modes allows it to be used as an IDS as well as an IPS. When you use Snort as a packet sniffer only, it provides you with a live readout of packets as they travel through the network. For packet logging, it records the packet details to a file as logs. It can detect attacks as buffer overflows, stealth port scans, CGI attacks, SMB probes, and OS fingerprinting attempts. It uses different methodologies (called “rules”) for performing intrusion detection. These rules work differently to signature-based detection, detect the actual vulnerability, rather than an exploit or a unique piece of data. Essentially, Snort uses a “known bad” or “suspected bad” approach when it comes to detecting intrusion.
When you use Snort, you apply these rules to the network traffic. You can download some of these rules, called “base policies” from the Snort website, or learn how to use Snort yourself and write your own. The Snort community website also has people who can help you to write and download rules developed by other Snort users.
Snort also works with companion applications, called Snorby, BASE, Squil, and Anaval. These are all intended to provide deeper analysis of the data Snort collects, which can make up for some of the shortfalls in the Snort software. However, it requires a lot of configuration before it can be used effectively and may not be suitable for someone unfamiliar with this kind of software. It can also be a bit tricky to update your rules, as you have to do so manually or via your script.
3. Suricata
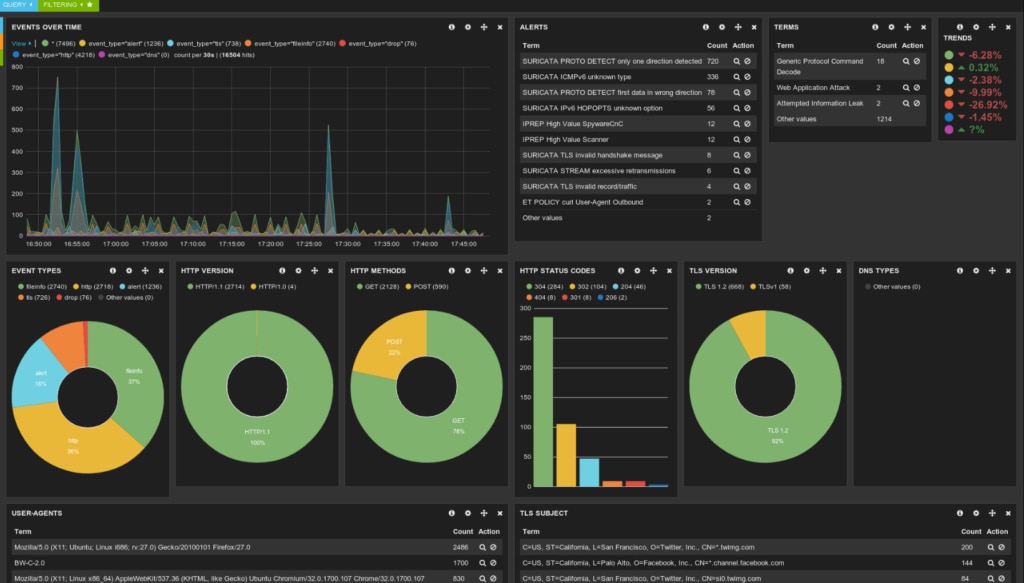
Another free but high-quality tool is the Suricata IDS/IPS. It works as a NIDS and uses a complete signature language to determine known threats, and what kind of behavior is likely to come from an intruder. One instance of Suricata can inspect multi-gigabit traffic, and the engine is built around a modern and scalable code base designed to perform at a high level.
It automatically detects protocols on any port and can apply detection logic to each packet and protocol as it comes through. As part of this, it can log HTTP requests, which can help detect scanning or flooding attacks using large numbers of “normal” protocol requests to overwhelm a network.
Alongside the NIDS engine, it also includes a NIPS engine to create alerts, filters, and apply thresholds or rate limits. It works with protocol decoders, including support for packet decoding with IPv4, IPv6, TCP, UDP, and many more, and protocol decoding at the app layer decoding for HTTP, SSL, TLS, SMB, DCERPC, SMTP, FTP, SSH, DNS, and so on. It can detect malformed code or requests using protocol keywords, rule profiling, file matching, pattern matching with machine learning, and extensive tuning options.
Suricata is intended as another open-source IDS competing with Snort, and it does have some advantages over what Snort can offer. First, Snort is single-threaded while Suricata offers multi-threading support and capture accelerators. However, Suricata suffers from a lack of documentation, which can make it difficult to troubleshoot or figure out how to use it if you’re unsure of the configuration.
4. Trend Micro TippingPoint
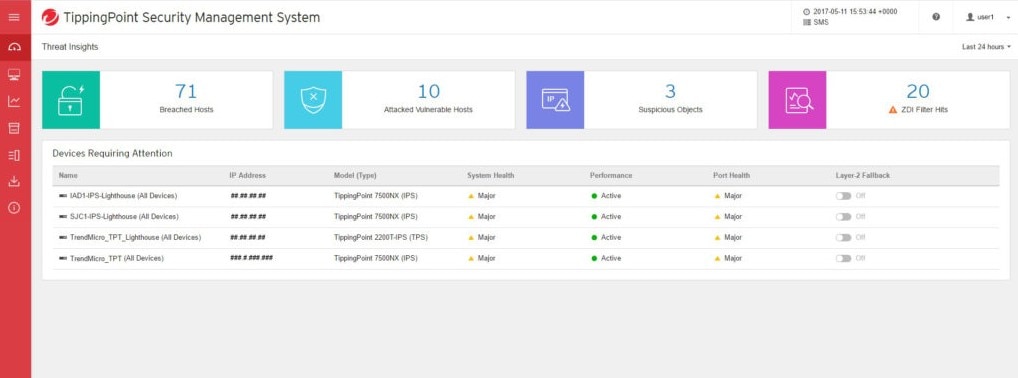
Trend Micro TippingPoint is an intrusion detection system with automated threat detection and response. It has both IDS and IPS capabilities. Its primary aim is to protect enterprises from ransomware, malware, and other kinds of attacks. It includes features such as virtual patching, shielding against vulnerabilities, and blocking exploits, and can also defend against known and zero-day attacks with high accuracy. It uses machine learning techniques to keep on top of threats and predict and react to attacks in real-time.
It also integrates with third-party applications to keep its list of known vulnerabilities and assessments up to date, including information from Rapid7, Qualys, and Tenable. It maintains high availability, so you always have your system working, using swappable power supplies, built-in inspection bypass, and watchdog timers to continuously monitor security and management engines.
Remember the “asymmetric routing” issue I mentioned above? The TippingPoint system inspects all kinds of traffic, including asymmetric traffic, and applies security policies to ensure comprehensive protection, as this kind of traffic asymmetry is widespread and pervasive throughout enterprise and data center networks.
Finally, it includes virtual patching capability, preemptive coverage between when a vulnerability is discovered and a patch is created for it. It uses vulnerability-based filters to effectively create a barrier between your network and any attackers who might try to exploit this vulnerability.
It can be used with Windows or Linux through a Java-based GUI called the Security Management System. For the pricing of TippingPoint, you need to contact Trend Micro for a quote, and they use a pay-as-you-grow approach with flexible licenses.
5. Cisco Stealthwatch
 Cisco Stealthwatch is a HIDS intended for enterprise use. This visibility and network security tool provides threat detection and response using machine learning and entity modeling. It also uses a unique behavioral analytics approach to provide you with visibility across your network, including all endpoints, data center, and cloud. It can continuously monitor and detect threats originating from within or bypassing existing security.
Cisco Stealthwatch is a HIDS intended for enterprise use. This visibility and network security tool provides threat detection and response using machine learning and entity modeling. It also uses a unique behavioral analytics approach to provide you with visibility across your network, including all endpoints, data center, and cloud. It can continuously monitor and detect threats originating from within or bypassing existing security.
It can also detect malware in encrypted traffic without needing to decrypt the traffic. This can ensure policy compliance when private data is concerned.
It responds quickly by focusing on critical issues and using a comprehensive knowledge of threat activity, and integration with current security measures in your system. For any threat detected, you can examine information including user, device, location, timestamp, application, etc.
Stealthwatch also uses analytics and machine learning to detect threats before they become an issue via anomaly detection. Any anomalies discovered are further analyzed with machine learning techniques and correlation with the local-to-global threat information. This combination allows organizations to detect unknown or encrypted malware, insider threats, and policy violations.
This cloud-based SaaS can be used with Windows, Linux, or Mac OS devices. You can trial the Stealthwatch for two weeks for free. After that, you need to request a quote to get a price for the software.
6. Darktrace Enterprise Immune System
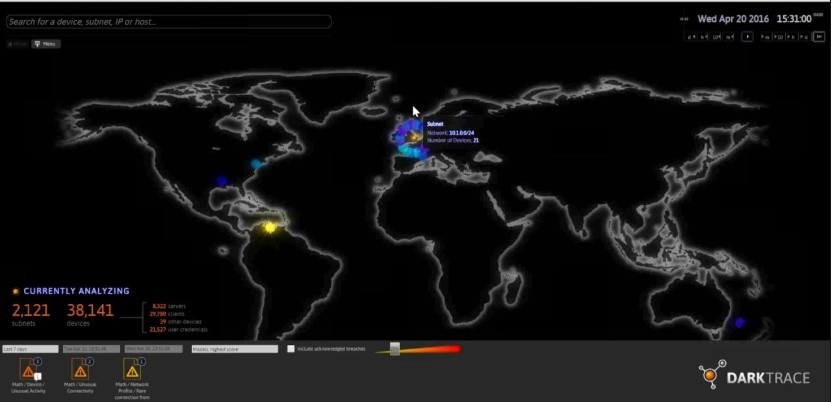
Darktrace Enterprise Immune System is an AI-based self-learning system to detect attackers and malicious entries to your network at an early stage. It works as a HIDS by learning what “normal behavior” looks like on your network, then continuously analyzing network and file-system behaviors to determine whether a change is alarming.
It can spot the signs of an attack at the beginning, without needing to rely on rules, signatures, or prior assumptions. It’s intended to detect in-progress threats, such as IoT hacks, insider threats, or latent vulnerabilities in your system. It then uses the Darktrace Antigena system to mitigate the threat, such as by slowing down or stopping a compromised connection or device.
One of its interesting features is called the Threat Visualizer, which is a real-time graphical interface with a 3-D view of threats to your enterprise. It displays threat alerts and includes a day-to-day overview of what your network usually looks like. This makes the software easy to use and more accessible for business executives (not just security specialists).
While Darktrace is accessible and good-looking, it’s light on features. It doesn’t provide a huge number of possible responses to threats, and it doesn’t include NIDS capabilities.
Darktrace offers a 30-day free trial.
7. OSSEC
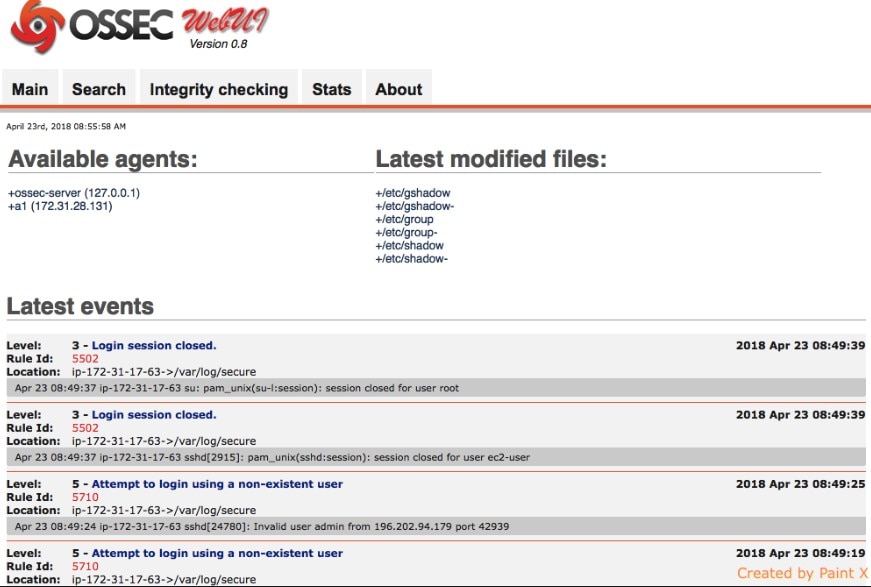
Open Source HIDS Security (OSSEC) is the leading HIDS, and it’s completely free. It focuses on your log files and file system changes in the computer where you install it. Then once it has taken a “snapshot” of your system and log files, it monitors those signatures and files to check for whether any changes have taken place, and whether those changes are legitimate. It will also examine attempts to get into or modify the root account on Unix systems, and on Windows it keeps your registry secure.
It’s an open-source project, but like the TippingPoint software above, is owned by Trend Micro. The OSSEC application can centrally manage several hosts in one main console, but can only be installed on Unix systems or Unix-like systems, including Unix and Linux distributions, as well as Mac OS. A Windows agent allows Windows computers to be monitored, but OSSEC cannot be installed on it.
You can use other applications as a front-end to the OSSEC data-gathering application, like Graylog, Splunk, and Kibana.
OSSEC collects data on web server activity, as well as mail and FTP files, keeping an eye on what comes in and out of the network. It also monitors traffic and antivirus logs and tables, as well as firewall activity and system event logs. You can determine what OSSEC flags and monitors by choosing policies or rules to install, which determine the conditions under which an alert occurs. You can display these alerts within your central console or set it up to receive notifications in your email inbox.
The user community for OSSEC helps develop and create these policies, and they’re readily available once you join the community and figure out how to use the product. The learning curve for OSSEC is a little steep, but if you’re prepared to become a part of the community and put in the effort, you can use it to its fullest abilities.
While OSSEC itself is free, Trend Micro offers paid support for OSSEC.
8. Zeek
Zeek used to be known as Bro. This NIDS includes other network monitoring functions beyond intrusion detection. It’s free to use, and the community of Zeek users includes a lot of academic and research-based institutions as well as businesses.
Zeek uses two separate steps to deal with intrusion detection, including both traffic logging and separate analysis. Since this is another free and open-source IDS distributions, it’s often compared to Suricata and Snort. Both Suricata and Zeek have an advantage over Snort due to their operation at the application layer, which gives you a higher-level analysis of packets and network protocols in use.
It reduces packet streams into events and looks at what’s happening, then uses scripts to determine how to respond. You can also customize these scripts. This allows you to decide how you want to be alerted to problems and includes the ability to log data for later use and execute programs on demand. With Zeek, you can also get a quick and broad overview of your network activity, including network devices, file types on your system, and software installed or in use. This information can then be exported to visualization tools to help you to make sense of the data.
Zeek has two separate tools as part of the signature analysis and anomaly detection. First, the event engine looks for events capable of triggering an alert, including HTTP requests and new TCP connections. All these events are logged and provide a list you can look at later to see if the actions themselves are normal, but the amount or frequency is suspicious. Like other tools, the second part of Zeek uses policy scripts. These scripts can be customized but generally use anomaly detection, signature matching, and connection analysis processes.
Zeek allows you to track HTTP, DNS, and FTP activity as well as SNMP traffic, and you can have as many active policies as you like running at the same time. You can also detect DDoS SYN flood attacks and port scanning using Zeek. The main downside with Zeek is you need to configure all the scripts yourself, which can be a lot of work.
Zeek is available in versions for installation on Unix, Linux, and Mac OS.
9. Samhain
Samhain is a free HIDS to check file integrity, monitor log files, and monitor ports. It can be run on a single computer, or on many different hosts. It provides centralized data gathering and analysis of the information collected by each individual machine.
Each individual agent of Samhain checks file integrity and monitors ports as well as log files. Samhain also checks for unusual or incorrect user access rights, as well as hidden processes and rootkit viruses.
If Samhain is working with a multi-host implementation, it applies encryption to the information and communication passed between each agent and the central controller. The monitoring process itself is protected from attack in this way, as well as by including authentication requirements when log file data is passed between hosts and the controller.
You can detect intrusion of your network using warning signs and information flagged by Samhain. However, this isn’t an IPS system and doesn’t prevent the intrusions from happening. As a result, you’ll need to keep backups of your user identities and system configuration if a problem flagged by Samhain ends up taking over your system. It might be more suitable for a smaller system than a large enterprise with significant amounts of data or uptime needs.
Samhain uses a kind of stealth technology called “steganography” to keep its processes hidden from attackers, which stops intruders from killing the IDS itself. This adds an extra layer of protection to your system.
This free and open-source piece of software is compatible with Unix, Linux, and MacOS.
IDS Configuration and Use Best Practices
Once you have chosen your IDS, make sure you follow best practices when it comes to its use.
First, baseline or profile what normal behavior looks like for your network. When you deploy and set up your IDS, this baseline is important for determining what abnormal or malicious behavior looks like. This baseline and abnormality will differ from network to network. Setting up clear baselines will save you time later and prevent false positives and false negatives if your network has slightly unusual “normal” behavior. An improperly set up or tuned IDS will send many false positives, which can result in huge overheads for your security and administration team.
Change defaults where necessary, as each network will be different. Your IDS should be aware of all relevant devices and applications, as well as which points on your network are critical to security. Especially when using custom devices or applications, you might need to configure your IDS differently from what a manual or guide suggests.
Next, make sure you have placed your IDS correctly. Deploy it in the highest point of visibility to not overwhelm the IDS with data, and then work down into your network. They’re commonly deployed behind the firewall but on the edge of your network. You can also install multiple IDS across your network to deal with intra-host traffic.
Make sure you have a clear and thorough understanding of your device inventory and what’s on your network. Understanding what each device is for, its role, how it functions, and its vulnerabilities will help you set up your IDS correctly for each part of your network and how it behaves.
Final Thoughts on Using an IDS System
Purchasing and setting up a high-quality IDS is vital for your organization’s network security and protection. Always ensure you have considered the threats your business is vulnerable to, with a clear understanding of the different kinds of attacks your system may be subject to.
I recommend SolarWinds SEM as a leading intrusion detection system available today, as it has comprehensive and robust tools for HIDS capabilities as well as a well-functioning and easy-to-use link with Snort packet sniffing. This way, you get a HIDS and NIDS all-in-one unified threat management tool.
Further Reading
IDS vs. IPS: What’s the Difference? For further information on the details and differences between IDS and IPS, check out the guide I wrote on this topic.
What Is HIPAA Compliance? For HIPAA-specific compliance, auditing, and security information, look into the requirements of HIPAA and what security measures you need to have in place to comply.
What Is a Data Breach? Ultimate Guide to Cybersecurity Breaches More information on data breaches can be found here, including what they are, how to prevent them, and how to respond if you’re the target of an attack that leads to a data breach.


