In the past few years, network topology and design have grown more complex with the evolution of point solutions, virtualization, distributed computing, and hybrid cloud models. Simple networks don’t meet the requirements of modern infrastructure anymore. To ensure your network delivers the expected performance, including good bandwidth speed, uninterrupted communication, and high availability, you need an end-to-end network monitoring strategy.
Let’s dig deeper to understand network monitoring and how it helps you optimize your overall network performance.
What Is Network Monitoring?
Your organization needs various network amplification devices such as routers, wireless access points, gateways, modems, ethernet cables, switches, repeaters, hubs, and more to provide good network connectivity and performance to the workforce. Emerging technologies like wireless, IoT (internet of things), cloud, and VPN have broadened the networking spectrum for data transfer, mobile or remote communication, and service delivery. Network elements and devices have also evolved from flat switches to multilayer switches, proxy servers, bridge routers, firewalls, protocol converters, and so on.
Despite this transformation, monitoring how well or efficiently your network is performing remains a critical factor. Network monitoring is the continuous analysis of a computer network or the entire network infrastructure using a system for discovering any slow or failing elements across the network. Once the issues are detected, network administrators are notified about these failures immediately via alerts (email, SMS, or other means), so they can take the required actions. The process of network monitoring falls under the network management umbrella.
Real-time monitoring gives your network admins complete visibility into your network infrastructure and allows them to identify the problems and their root causes or origins. Knowing what’s going on in your network is critical to ensure business continuity. Your network’s performance depends on various elements of your network topology. These include:
- LAN (Local Area Network), WAN (Wide Area Network),
- VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), multilayered connections, MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
- The state of network nodes, such as the access or distribution
- Tandem switches, servers, routers, firewalls, client computers
A properly configured network monitoring system continuously monitors your network inside out and looks for the issues caused due to internal failures such as server crashes or overloaded devices.
Modern monitoring software or programs perform regular tests to check your web server status by sending HTTP requests for retrieving a web page. Similarly, test email messages are sent using SMTP and fetched back through POP3 or IMAP to check if email servers are working as expected.
The following factors are essential for analyzing and measuring your network performance:
- Uptime, responsiveness, or availability
- Bandwidth and throughput
- Network latency, reliability, and consistency
- WAN efficiency
- Measurement of round-trip delays
Advanced monitoring systems generate predefined actions when there are failures in connection establishment, timed-out requests, or failed attempts to retrieve a document or message. Automated activities include alerts to the concerned admins, activation of failover systems for eliminating problematic servers, proactive blocking of potentially vulnerable network points or elements, and more.
To measure your inbound and outbound network traffic, you need to monitor the performance of uplink in your network environment.
Key Aspects of Network Monitoring
Outlined below are some critical measurement areas in network monitoring:
- Internet Server Monitoring: Internet server monitoring tools continuously check web servers and alerts the server hosting provider or your internal admin team if any of the network servers go down. Server monitoring can be both internal and external.
- Protocol Monitoring: Network monitoring services check and test various types of protocols—SNMP, SMTP, HTTPS, FTP, DNS, POP3, UDP, IMAP, SSL, TCP, TELNET, ICMP, SIP, and other network ports at predefined time intervals.
- Network Tomography: Network tomography uses end-to-end probing to monitor the health of your network links. The UDP probe packets are sent by agents to responders at various network points.
- Route Analytics: Route analytics is the monitoring of network routing postures and identifying performance issues causing downtimes or latencies in your network, using advanced systems, algorithms, and tools.
Best Network Monitoring Software
SolarWinds® Network Performance Monitor (NPM) offers end-to-end monitoring for your multi-vendor networks, including deeper, valuable insights and intelligent network mapping. NPM allows you to start small (from monitoring a single computer network) and scale up as your networking environment expands over time.
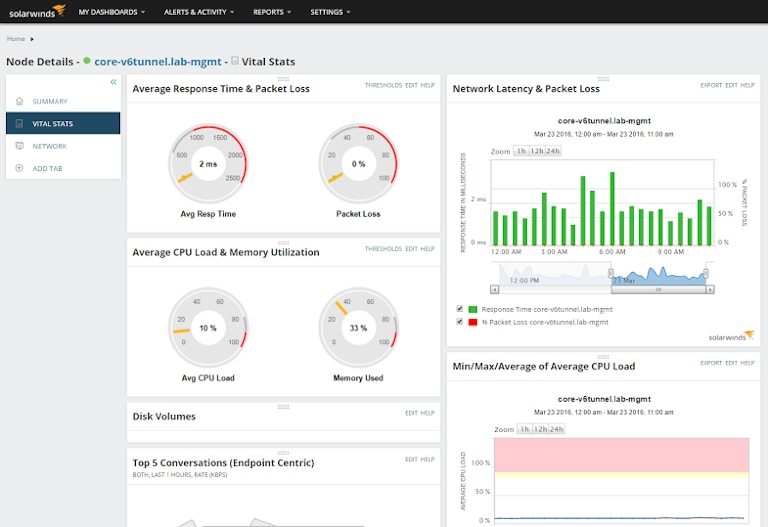
NPM helps you ensure your content or services are seamlessly delivered to your users with detailed path analysis of critical networks. Its all-in-one dashboard gives you a clear picture of all your networks, vendors, devices, and applications along with their path analysis, allowing you to separate signals from noise and eliminate downtimes.
SolarWinds also provides the NetPath™ and PerfStack™ features with Network Performance Monitor for easy troubleshooting of performance issues across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments. Its advanced alerting capabilities filter out noise from the signals and notifies you about network troubles. You can easily create custom alerts by defining specific trigger rules, so your admins receive only actionable, informative alarms.
NPM’s auto-generating network visualization capability provides a unified view of all your network connections, topologies, dependency relationships between network devices, and detailed information on add-drop multiplexer (ADM). The network visualizer also helps you build dynamic charts, maps, and graphs of your network infrastructure. With meaningful insights into the current status of your network, identifying critical problems and fine-tuning network health becomes easy.
Additionally, NPM gives you in-depth visibility into how well your VPN tunnels are performing, including the overall health of your Cisco ASA environment. You’ll know when tunnels are down, restricting users to access business-critical network services so you can ensure seamless connectivity between sites.
Leveraging SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, you can easily monitor and analyze a software-defined networking (SDN) environment within a single pane of glass, including physical and logical elements such as:
- Multi-tenant networks
- Application policy infrastructure controllers (APICs)
- Endpoint groups
- Nodes
- Application profiles
Its network performance monitoring capabilities also include automated mapping of VPCs, physical ports, and port channels across your network switches to help you identify problems in your VPCs and ensure network availability. NPM enables network admins to find out and isolate the root causes of network outages and load balancing failures from your infrastructure. This helps you monitor and optimize the performance of all your network components contributing to application delivery.
Try out SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor to simplify your network performance monitoring.
