Technology plays a vital role in our daily lives in today’s interconnected world. Network-related challenges are drastically surging, resulting in a high rise of web-related problems. These kinds of issues highlight the need for effective network mapping solutions. Network mapping is the process of creating logical and visual maps to visualize and understand the interconnectivity of network devices, which provides in-depth visibility into enterprise IT infrastructure.
In this article, you’ll learn different topologies used to create network diagrams and key features to consider when implementing visual maps. And, most importantly, we’ll discuss the top seven tools for network mapping and monitoring.
Logical Network Diagram vs. Physical Network Diagram
Key Network Mapping Software Features
7 Best Network Mapping Software Tools
1. SolarWinds Observability Self-Hosted (formerly known as Hybrid Cloud Observability) (Free Trial)
2. SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (Free Trial)
4. Datadog Network Performance Monitoring
6. Paessler PRTG Network Monitor
Types of Network Topology
Topology refers to the arrangement of nodes and connections in a network. Nodes mean different devices like routers, modems, switches, etc. that we use in a network. We use different types of topology to pass the data from one node to another node. There are six main types of topology.
Bus Topology
In bus topology, every device is connected to a single communication channel or cable (bus). The data travels in one direction; however, it creates a single point of failure when the network grows. In a bus topology, every device receives the transmitted data, but only the intended recipient can process it. It’s simple to set up, requires minimal cabling, and is less expensive. This type of topology is usually used to implement LAN networks. In bus-based networks, coaxial or twisted pair cables are typically employed.
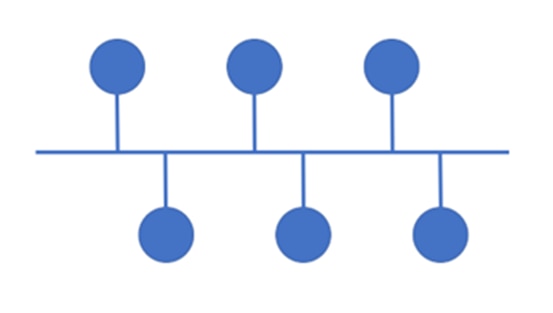
Star Topology
In star topology, all the devices are connected to a central hub or switch. The center point acts as a communication hub from which data transmission takes place to any recipient. It’s also used in LAN networks as it is inexpensive and easy to install. But if the central hub creates any issues, then it can disrupt the entire network.
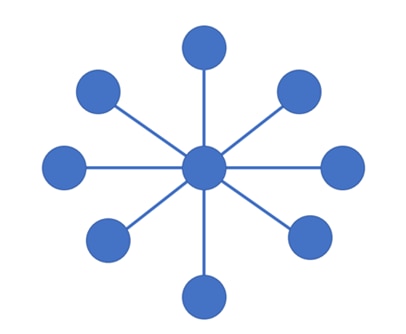
Ring Topology
In a ring topology, the devices are connected in a circular manner, where each device constructs a connection with two devices. If two devices need to communicate with each other, then they can do so directly if they’re neighbors. But if the nodes are not neighbors, then the sender and receiver nodes have to rely on their neighbors for communication. Thus, repeaters are employed in ring topologies with a lot of nodes since data must go through all of them in order to reach the last node. Thus, repeaters are used to stop data leakage.
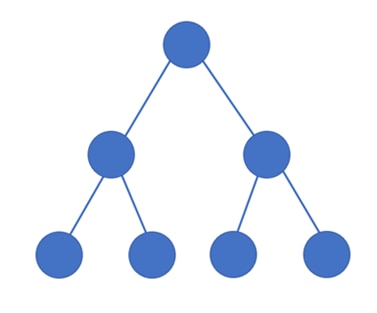
Tree Topology
A tree topology combines the characteristics of star and bus topology. It follows the hierarchical order consisting of root and leaf nodes and is also known as hierarchical topology. All other nodes are descendants of the root node, which is the topmost node in a tree structure. And the nodes that do not divide further are known as leaf nodes. There is only one path that exists for the transmission of data between two nodes. Broadband transmission is a good application of tree topology. The new device can easily be added to the existing network architecture. Error detection and troubleshooting are easy in tree topology. And a breakdown at one node doesn’t affect the entire network.
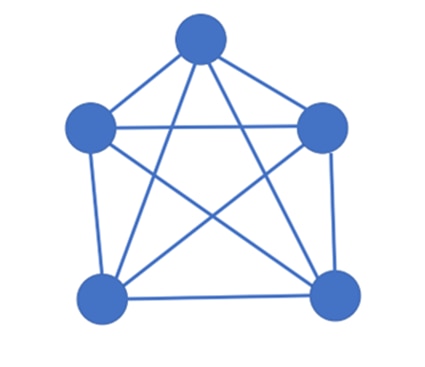
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology follows a simple architecture where each device is connected to every other device in a network that forms multiple paths to reach any other node from any source node. In this network, the device can directly communicate with other nodes without having to depend on intermediate nodes. Mesh topology is widely used in wireless networks such as WAN implementation where communication failures are a critical concern. The best example is the internet.
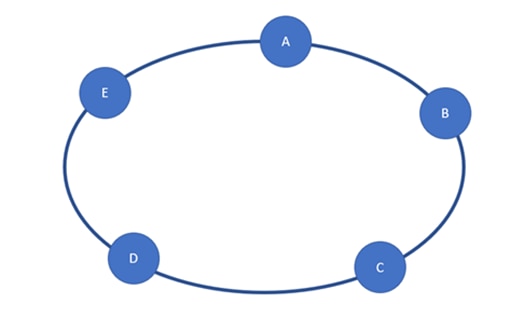
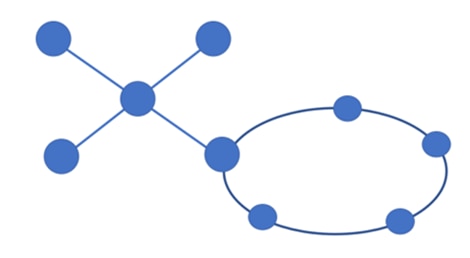
Hybrid Topology
The combination of two or more different topology types is known as hybrid topology. A hybrid topology connects several links and nodes in order to transport data. Hybrid topology enjoys the pros of each type of topology; thus, organizations use it to meet specific network requirements, leveraging the strength of different topologies to create a more flexible network infrastructure.
Logical Network Diagram vs. Physical Network Diagram
A logical network diagram emphasizes logical relationships between its components with the help of a conceptual representation of network architecture. It mainly focuses on the data flow, data transmission protocols, and logical addressing scheme. It abstracts the physical layout and presents a high-level view to explain the device communication within the network.
On the other side, a physical network diagram provides a more detailed description of network architecture to explain its physical infrastructure. It showcases the exact hardware location, network types, equipment, and data transmission cabling. With the help of a physical network diagram, one can get an idea of physical connections between the devices and how one node can communicate and pass the data to any other node.
There are different factors on which we can differentiate a logical network diagram and a physical network diagram.
- Focus: A logical diagram provides the logical relationships and data flow conceptually, while a physical network diagram provides the physical layout and actual nodes connection architecture.
- Abstraction: A logical network diagram provides a conceptual view after abstracting the physical view. In contrast, a physical network diagram provides clear and specific details about physical elements.
- Representation: A logical network diagram utilizes symbols and icons to illustrate the network components like servers, databases, protocols, cables, subnets, etc. On the other hand, the physical network diagram uses detailed images to represent different network devices and pieces of equipment.
- Change over time: A logical network diagram tends to remain relatively stable even as physical components are added or replaced. But the physical network diagram needs regular updates to reflect new changes in network infrastructure.
Key Network Mapping Software Features
There are several network mapping software tools available on the market, and each one poses different features. The right mapping software will give you a comprehensive view of mapping network architecture. Let us explore some key features that network mapping tool should have.
- Automated network discovery: A network mapping software helps visualize the interconnectivity of devices in a network. It should also provide automated discovery to identify and map devices across the network, which saves lots of time in manual configuration.
- Real-time monitoring: Real-time monitoring helps track network changes and updates, receive alerts, and address potential issues to ensure network stability.
- Device tracking: The tool helps to keep records of devices including IP addresses, physical locations, and ongoing activities.
- Network performance metrics: The software should provide essential performance metrics such as bandwidth utilization, packet loss, and latency for better optimization.
- Customizable maps and reports: A network mapping solution should report information in a visual way and present it concisely so users get clear information about current network performance.
- Interaction with other tools: One great feature that any software provides is the ability to integrate with other tools. With the help of other monitoring tools, you can enhance network visibility and streamline the workflow.
- Mobile accessibility: It allows users to monitor and manage the network on the go, ensuring quick response to critical issues.
- Historical data analysis: This feature allows users to analyze long-term trends, plan any maintenance or updates, and perform root cause analysis.
7 Best Network Mapping Software Tools
Now that we’ve discussed the key features to look for in network mapping tools, let’s explore the seven best network mapping software solutions. This will help you choose the best network mapping tool for your organization.
1. SolarWinds Observability Self-Hosted (formerly known as Hybrid Cloud Observability) (Free Trial)
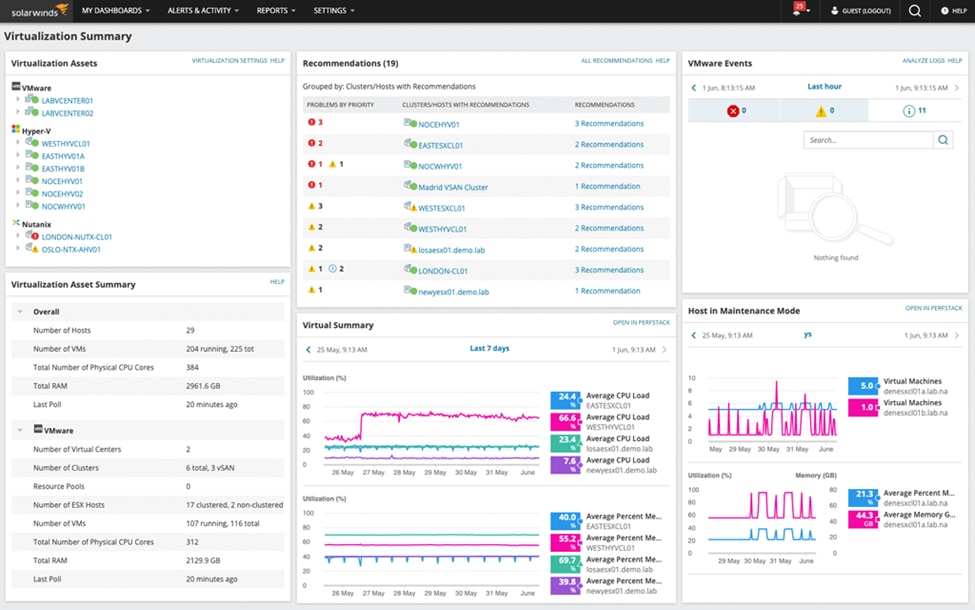
©2023 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
SolarWinds Observability Self-Hosted (formerly known as Hybrid Cloud Observability) is an advanced network mapping and monitoring software service designed for hybrid IT environments. It offers deep visibility into both on-premises and cloud-based resources that help manage and optimize hybrid networks. It also allows users to create customizable dashboards to monitor specific key performance indicators (KPIs). Some of the key features of SolarWinds Observability Self-Hosted (formerly known as Hybrid Cloud Observability) are:
- Identification of resource optimization opportunities that lead to cost savings and improve efficiency
- Root cause analysis
- Integration with cloud providers
- Alerts and remediation system
Learn More Download Free Trial
2. SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (Free Trial)
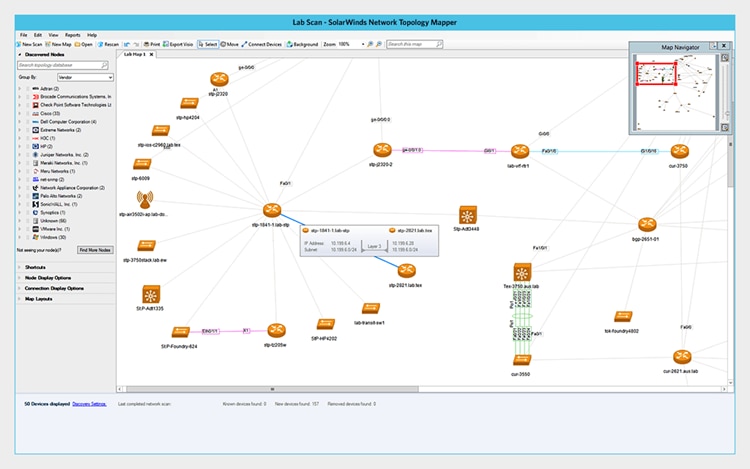
©2023 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
Network Topology Mapper (NTM) is a specialized network mapping solution that provides automated and intuitive mapping solutions for both small- and large-scale networks, which is best for small to large businesses. NTM can automatically identify and map the entire network topology, displaying the structure and making it easy to understand how each device connects. It provides flexibility to perform manual configurations and modifications whenever necessary. Below are some of the main features of SolarWinds NTM:
- Visual network representation
- Several discovery method options including CDP, SNMP, VMware, ICMP, WMI etc.
- Network change tracking
- Dependency analysis
- Scheduled network scans
- Using a single scan to build numerous maps
3. Nmap
Nmap is a free, open-source, and powerful network scanning tool usually used for network exploration and security auditing. It’s designed to identify hosts and open ports on computer networks, which provides great insights for network administrators, security professionals, and technical developers. It makes use of IT packets to determine hosts, services, firewalls, and other useful information. The main features of the Nmap tool are as follows:
- Host discovery and port scanning
- Version detection
- Output customization
- Various scan techniques
- Flexible target specification
- Community support and updates
4. Datadog Network Performance Monitoring
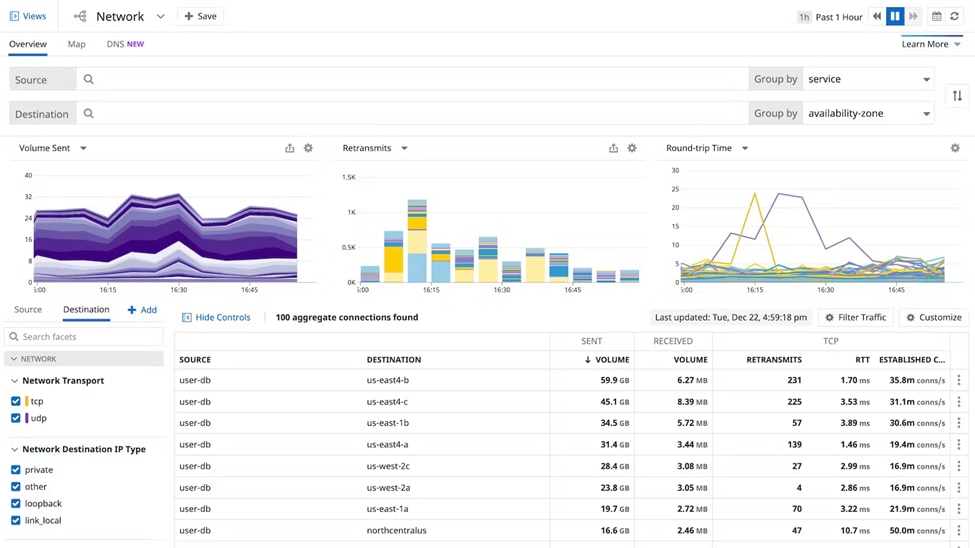
© Datadog 2023
Datadog Network Performance Monitoring (NPM) is a cloud-based service designed to provide real-time visibility and analysis of network performance across distributed environments. It offers a range of network monitoring utilities for both cloud-based and on-premises networks. With the help of Datadog NPM, you can actively monitor network issues, as well as infrastructure metrics, logs, and traces, ensuring optimal performance and reliability of the network for digital businesses. Some main features of the Datadog tool are:
- Agent-based data collection
- Real-time network monitoring
- Performance monitoring for both cloud and on-premises networks
- Automatic topology mapping
- Anomaly detection
- Centralized and user-friendly console
- Network traffic filtering
5. ManageEngine OpManager
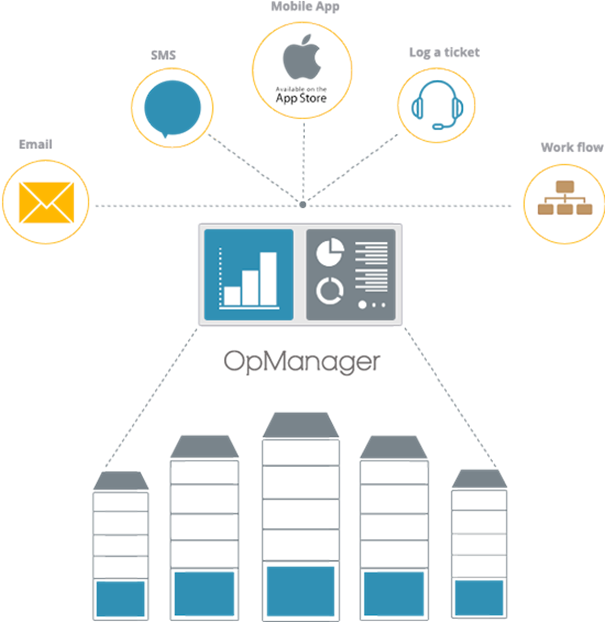
© 2023 Zoho Corporation Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
OpManager is an automated management solution designed to allow you to configure network maps with very little effort and time. It has a user-friendly interface and extensive feature set, which enables users to actively monitor, troubleshoot, and optimize network infrastructure. You can even create 3D visualizations of rack servers and topology maps. Some of the main features of the ManageEngine tool are:
- Configuration management
- Application performance monitoring (APM) integration
- Customizable network maps
- Network traffic analysis
- Performance thresholds and alarms
- Multi-vendor device support
6. Paessler PRTG Network Monitor
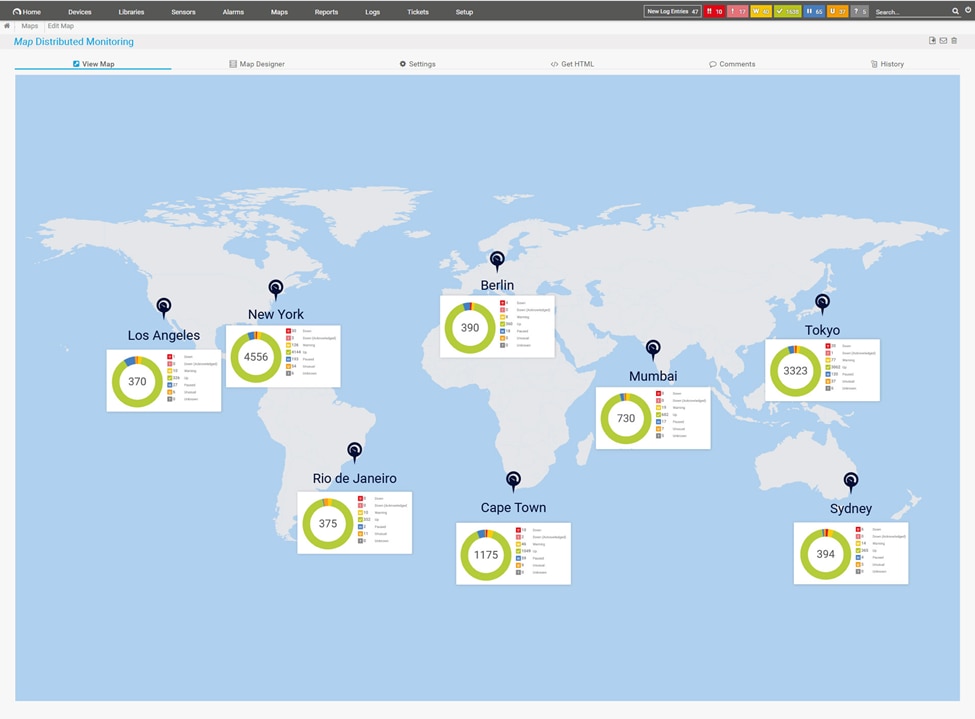
©2023 Paessler AG
PRTG Network Monitor is a network monitoring tool with a unique sensor-based approach designed to provide real-time insights into network performance. With an all-in-one approach, it simplifies network monitoring and enables smooth infrastructure management. Each PRTG sensor monitors a single component from thousands of sensors we have to choose from. The key features of the PRTG Network Monitor are as follows:
- Sensor-based monitoring
- Quality of service (QoS) monitoring
- Mobile access
7. Nagios
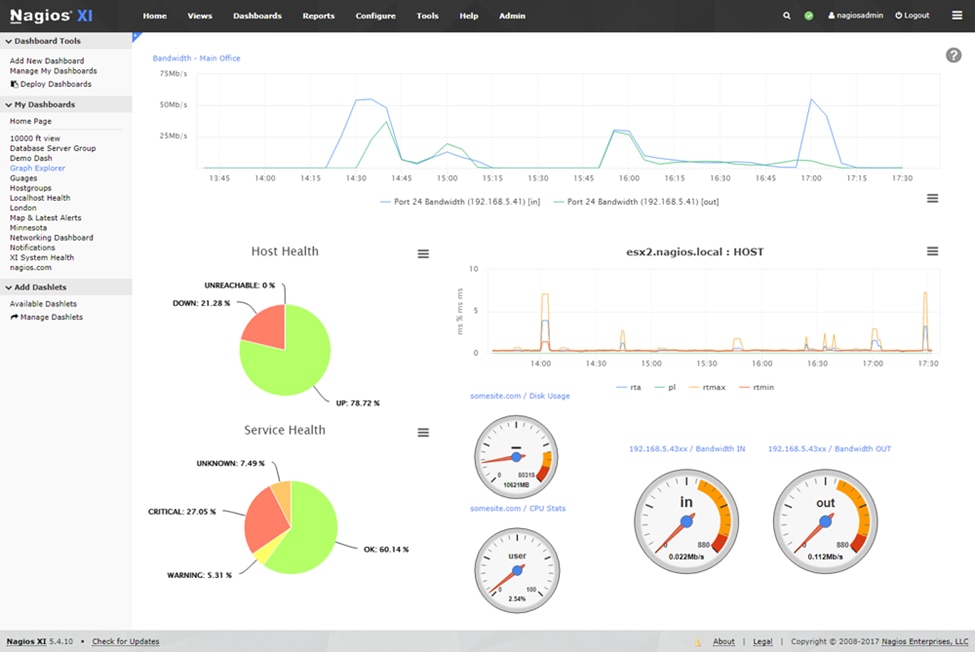
Copyright © 2009-2023 Nagios Enterprises, LLC. All rights reserved.
Nagios is another open-source network monitoring tool that provides comprehensive capabilities for network architecture, servers, applications, and services. It offers unparalleled flexibility for network administrators and IT teams to monitor and manage entire IT environments. The key features of the Nagios network monitoring tool are as follows:
- Plugin architecture
- Alerting mechanism
- Host and service monitoring
- Performance graphs
- Event handling and notifications
- Web interface
- Advanced reporting
Network Mapping – Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored the different network mapping tools along with their robust features and functionalities that empower businesses to keep track of interconnected devices in the network and troubleshoot network issues easily. SolarWinds offers powerful tools, Network Performance Monitor and SolarWinds Observability Self-Hosted (formerly known as Hybrid Cloud Observability), and stands out as a market-leading solution. With these cutting-edge mapping and monitoring tools, IT teams can tackle network challenges, optimize resources, and smooth operations for digital experience.
This post was written by Gourav Bais. Gourav is an applied machine learning engineer skilled in computer vision/deep learning pipeline development, creating machine learning models, retraining systems, and transforming data science prototypes to production-grade solutions.
