If you use a database, you’ll need to use a query language to communicate with and retrieve valuable information from your database. While there are many different query languages, Microsoft Structured Query Language, also known as SQL, is the most popular. Proactively monitoring and maintaining your SQL database can go a long way toward helping you optimize your SQL query performance. However, there are also several best practices you can follow to optimize SQL queries.
Databases are becoming increasingly large and more complex, making SQL database query optimization a top priority. In this article, I’ll discuss what SQL queries are and best practices for improving their performance.
- What Are SQL Queries?
- How Can You Select Which Queries to Optimize?
- What Are Some Best Practices for Optimizing SQL Query Performance?
- Using an MS SQL Query Optimization Tool
- Final Thoughts on Optimizing SQL Query Performance and Following Best Practices
WHAT ARE SQL QUERIES?
SQL stands for Standard Query Language, and it’s the most popular database query language. First developed in the 1970s and previously named Structured English Query Language (SEQUEL), SQL was designed to manage, organize, and extract data found in relational database management systems (RDBMS).
By using SQL, you can communicate with your databases. For example, if you need to retrieve specific information from a database, you can perform a SQL query. However, databases are limited by their hardware’s processing capabilities, which can result in slow queries. By engaging in SQL table optimization and reducing the number of calculations your software and hardware must perform, you can optimize SQL query performance and reduce their execution time.
HOW CAN YOU SELECT WHICH QUERIES TO OPTIMIZE?
Before you can optimize any queries, you have to decide which ones are best to optimize. Unfortunately, many people skip this critical step, but by targeting specific, troublesome queries with significant impacts on execution time, you can dramatically increase performance.
If you are less selective when deciding which queries to optimize, you may end up wasting time and money by optimizing those that don’t significantly contribute to performance, don’t impact other queries, or don’t result in problems users will notice.
When starting the MS SQL database query optimization process, look for queries that are consistently or occasionally slow, have red flags, or are major contributors to the total execution time.
Consistently Slow Queries
If you have a consistently slow query, it may be time to optimize it. When executed frequently, queries with high latency can cause performance issues, so it’s crucial to monitor and optimize them.

Occasionally Slow Queries
If a query is only occasionally slow, you may be wondering whether it’s worth the time, effort, and resources to optimize. Of course, the answer depends on which specific query is occasionally slow and whether its longer-than-average runtime is due to the query itself or something else. Sometimes a slow query can be the result of cache misses or poor overall server performance.
However, if you notice an occasionally slow query—whether you decide to optimize it or not—it’s a good idea to monitor it carefully. Slow queries can indicate small, potentially server-wide problems and may worsen over time. Occasionally slow queries can also be a sign of occasionally broken functionality or long-tail latency problems.
Queries With Red Flags
Even if you haven’t noticed any performance issues yet, you may want to optimize some queries. It may be time to optimize any queries that have returned warnings and errors. If a query doesn’t use indexes, consider optimizing it. By proactively optimizing queries, you can prevent issues from occurring in the first place.
Queries That Majorly Contribute to Total Execution Time
If more than five percent of total execution time can be attributed to a single query, try to optimize the query in question. Focusing your efforts on optimizing major contributors rather than those that don’t significantly contribute to performance will enable you to use your time more efficiently.
WHAT ARE SOME BEST PRACTICES FOR OPTIMIZING SQL QUERY PERFORMANCE?
Once you’ve identified which queries need improvement, it’s time to optimize them. As previously mentioned, reducing the number of calculations your software and hardware perform during a query can lead to optimal SQL query performance and a reduced execution time. Here are some tips and best practices for MS SQL database query optimization.
Define Your Requirements
When trying to find specific data, it’s essential to use an appropriate query, and the first step to finding the right one is deciding which data you want to retrieve. You should clearly define your requirements before writing the query, enabling you to receive only the information you need, potentially reduce runtime, and optimize SQL queries.
Reduce Table Size
SQL table optimization is an essential part of MS SQL database query optimization. To ensure you only receive the information you need, you can filter your data. Filtering data will reduce table size and optimize SQL queries’ runtime. Popular methods for SQL table optimization and query speed improvement include:
- Providing a limited range of dates for time series data
- Limiting the dataset in a subquery
- Avoiding duplicate data
Simplify Joins
Sometimes, when a query joins tables, it drastically increases the result set’s row count, which can lead to a slow execution time. Before joining tables, try to reduce their size, as explained above.
Something as simple as changing the order you join tables in can also optimize SQL queries. When joining two tables, start with the one that will return the fewest results after filtering.
Use SELECT Fields FROM Instead of SELECT * FROM
By using SELECT fields FROM instead of SELECT * FROM, you can narrow down the data fetched from the table during a query, increasing your query’s speed. The command SELECT * will fetch all the data from your table, whereas specifying fields can reduce query runtime by ensuring you only receive the necessary data.
Similarly, using SELECT ID instead of SELECT DISTINCT can reduce the processing power required to perform the query while still returning unduplicated records. For example, if you want to find a specific customer, the query SELECT DISTINCT John, Smith, Canada FROM Customers might return several results, as many people in Canada are named John Smith. SELECT DISTINCT relies on the GROUP BY clause, which requires a lot of processing power. To further filter your results and use less processing power, try SELECT ID, John, Smith, Canada, Manitoba, Winnipeg, R2C 0A1 FROM Customers.
Use EXISTS() Instead of COUNT()
Though you can use both EXIST() and COUNT() to discover whether the table has a specific record, using EXIST() is more effective. While COUNT() will search the entire table to provide the total number of matching records, EXIST() will only run until it locates the record’s first entry in the table, saving you time and computing power and enabling you to optimize SQL queries.
Use WHERE Instead of HAVING
Another SQL query optimization technique is using WHERE instead of HAVING. WHERE queries execute more quickly than HAVING queries. WHERE queries filter records before groups are created, while HAVING queries filter data from groups. As a result, using WHERE in place of HAVING is an easy strategy for SQL query optimization.
Add EXPLAIN to the Beginning of a Query
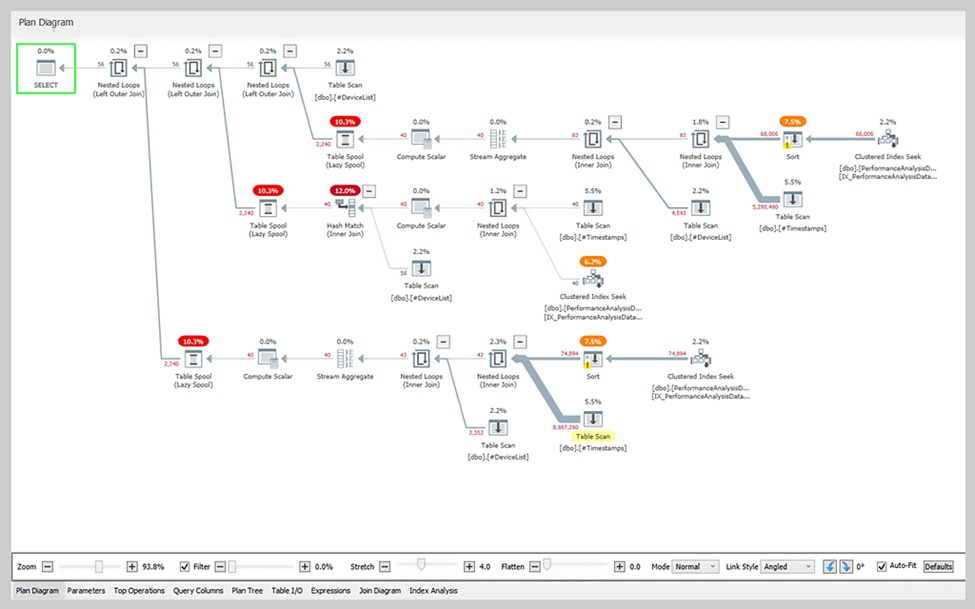
By adding EXPLAIN to the beginning of a query, you can view your query execution plan and get a better idea of how long your runtime will be. Though it’s not always completely accurate, your query execution plan will display both your query’s execution order and its cost (higher cost numbers signify a longer run time). To understand the order of execution, start reading your query execution plan from the bottom up.
When you insert EXPLAIN at the beginning of a query, you can locate and modify the most expensive steps. Then run EXPLAIN again to determine whether the changes you made significantly reduced runtime. However, running EXPLAIN takes time and computing power, so you should only use it during the MS SQL query optimization process.
Create SQL Server Indexes
You can retrieve data faster and optimize SQL queries by using clustered and non-clustered SQL Server indexes. Indexes can reduce runtime, but it’s also important to consider how much disk space they require.
In Microsoft SQL Server, you won’t need additional disk space for your clustered indexes. However, if you use non-clustered indexes, these indexes are stored separately and require more disk space.
In addition to knowing how to properly create indexes, it’s key to understand when not to use indexes. If you have an incredibly large range of values, it might be better to scan the whole table rather than use an index. In cases where functions or operations are applied to a column, you shouldn’t use indexes. You should also evaluate your existing indexes.
Avoid Running Queries in a Loop
Running queries in a loop can significantly slow your runtime. In some cases, you may be able to bulk insert and update data, which is far more efficient than using loops.
UNION ALL instead of UNION
The UNION ALL and UNION on a surface level does precisely the same thing. The difference between both statements lies in the duplicates.
While UNION joins both tables and returns only distinct records (it technically performs a DISTINCT on the table union result), UNION ALL will join the tables and return all returns, duplicates, and records included. This very reason makes the UNION ALL much faster than the UNION when one looks at it from the performance point of view.
However, this performance difference between both statements becomes less insignificant when considering the datasets’ size and complexity.
USING A MICROSOFT SQL QUERY OPTIMIZATION TOOL
If you know your system has poor performance and needs refinement, but you can’t locate what specific queries need to be optimized, using an SQL query optimization tool will enable you to quickly and accurately identify queries for optimization.
The query itself may not always be responsible for slow execution times, as other events occurring elsewhere can sometimes result in suboptimal performance. Without the help of an MS SQL query optimization tool, you may have difficulties differentiating between SQL queries in need of optimization and those that were simply slow at one point in the past due to other factors.
While you can find queries in the MySQL Performance Schema, PostgreSQL pg_stat_statements, and query logs, using an MS SQL query optimization tool can save you time and frustration.
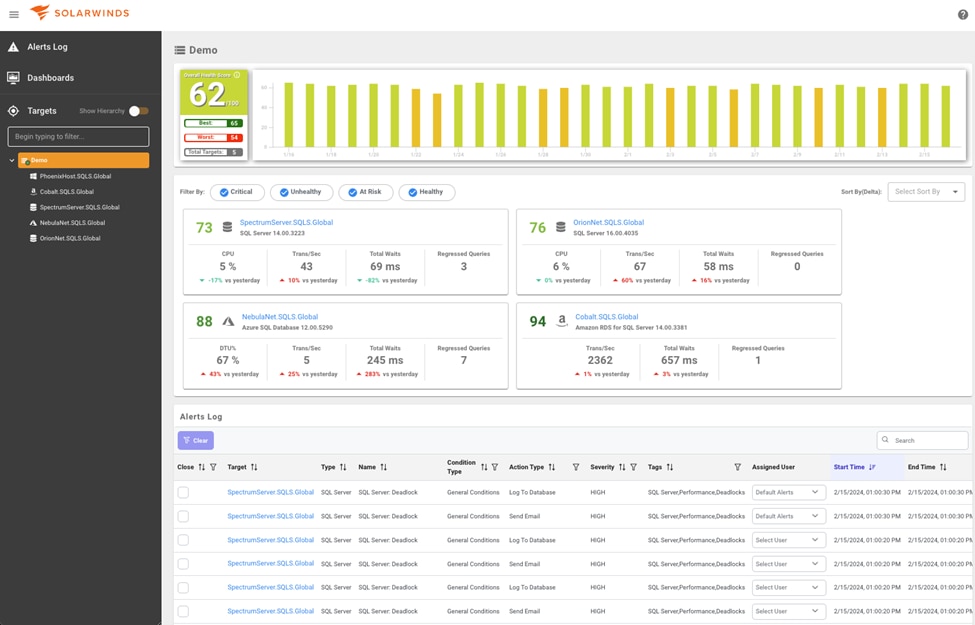
SolarWinds SQL Sentry
© 2024 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
SQL Sentry by SolarWinds optimizes physical, virtual, and cloud server environments on the Microsoft Data Platform, providing insight and awareness for performance issues. It empowers businesses to achieve breakthrough performance across data systems, regardless of size or location. With scalable monitoring, proactive alerting, and actionable performance information, SQL Sentry enables users to diagnose and optimize their entire SQL Server stack efficiently. Features such as Index Analysis and Optimization further enhance database speed and efficiency. SQL Sentry offers a free 14-day trial, providing customers with the confidence to tackle performance challenges and deliver real business value.
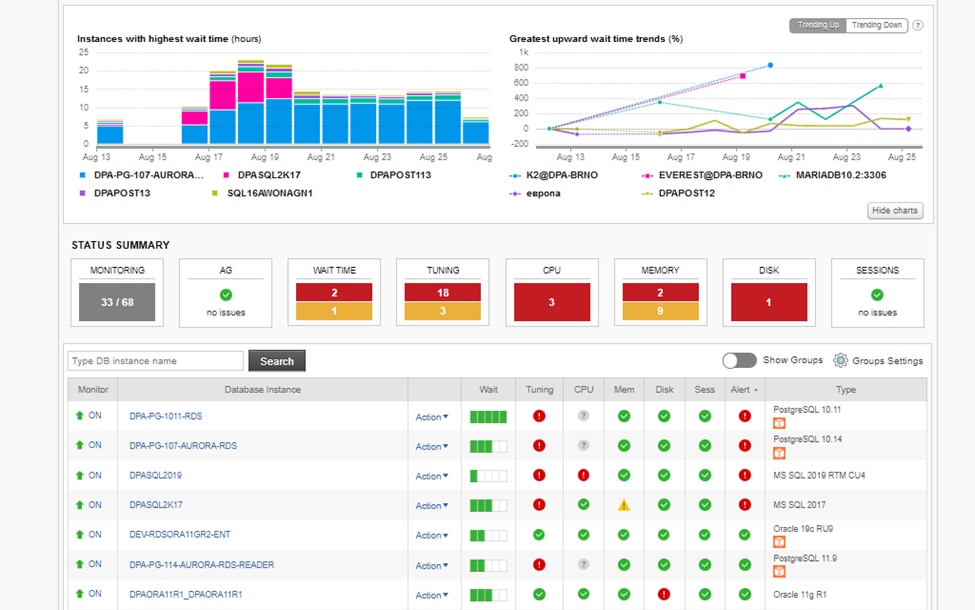
SolarWinds Database Performance Analyzer (DPA)
© 2024 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
DPA simplifies the process of monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing SQL query performance. Use the mass registration feature or the wizard to register database instances. Once DPA has been configured, you can easily find underperforming queries, tables, and applications. Then, you can move on to MS SQL database query optimization and SQL table optimization.
Thanks to DPA’s continuous, down-to-the-second SQL database monitoring, you can perform real-time and historical SQL query performance analyses to identify and solve performance issues. DPA also can make searching for, filtering through, and managing SQL query statements fast and easy.
Highly scalable, compatible with most common databases, and ready to support virtual, physical, and cloud-based databases, DPA can continue to support your organization as you grow or switch databases. You can integrate DPA data with SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor (SAM) via the Orion® Platform to access end-to-end monitoring throughout your servers and applications.
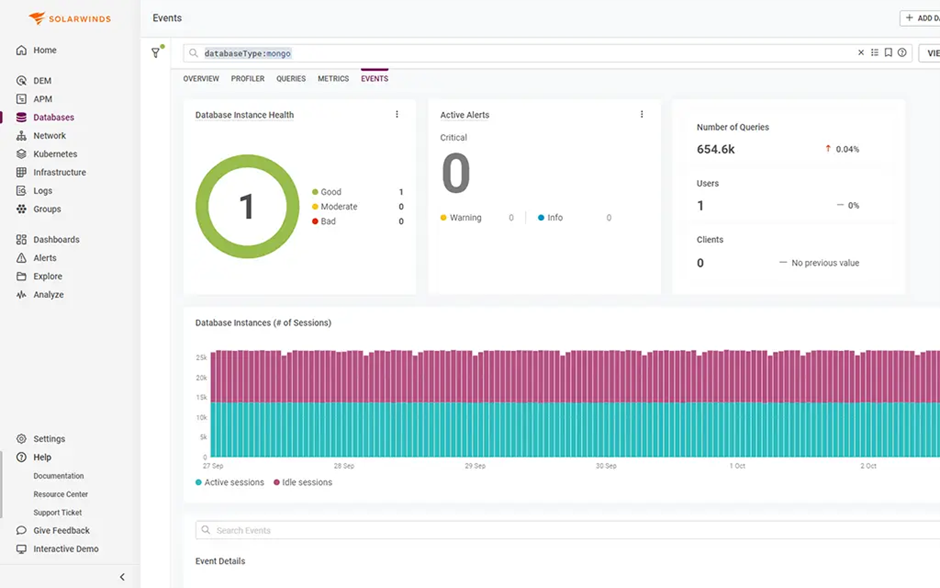
SolarWinds Database Observability (DBO)
© 2024 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
You don’t have to rely on slow query logs to capture traffic and monitor your database or worry about accidental downtimes or taking down your entire server when logs run for an extended time. Instead, use SolarWinds Database Observability (DBO), to gain better visibility into your databases and their performance.
Database Observability is designed to be inclusive— as it supports your traditional, open-source, and cloud-based SaaS databases. This way, you can quickly view key databases and query information from a centralized location, regardless of its source, simplified by taking advantage of DBO’s custom side-by-side views.
Curious about how this works? Our comprehensive Database Observability QuickStart talks about installing the SolarWinds Observability Agent on your host server and monitoring your databases through a unified view.
Features
Besides being robust and highly reliable, Database Observability simplifies database performance monitoring and MS SQL database query optimization. Monitoring SQL database performance with Database Observability is more efficient and thorough than using a slow query log. For example, slow query logs don’t track CPU usage and can only run for short periods, as they require an immense amount of storage. Database Observability, on the other hand, is built to offer 24/7 database performance monitoring, capture valuable information, and supply comprehensive database performance analytics. You can access query samples and explain plans or correlate query behavior with system metrics to troubleshoot performance issues and optimize SQL queries more efficiently. Also, since it is part of SolarWinds Observability, you get Observability-as-a-Service right on the platter, A strategy vital to your organization’s digital transformation strategy.
Thanks to its customizable alerts, daily summary reports, and weekly summary reports, you can stay on top of database performance with DBO and better understand the performance of your queries and your databases’ health.
SolarWinds Plan Explorer
If you are looking for a more cost effective option, Plan Explorer is a free tool designed to simplify the process of analyzing and optimizing query performance for SQL Server developers and administrators, Plan Explorer provides a user-friendly graphical representation of execution plans, highlighting operators with high costs and offering detailed breakdowns of query operators. By identifying performance bottlenecks and areas for improvement, users can optimize query performance more efficiently. Plan Explorer is easy to download, install, and use, offering a faster and more intuitive alternative to SSMS for query optimization.
WHY DO WE NEED TO OPTIMIZE SQL QUERY PERFORMANCE?
Optimizing your SQL queries is optimizing for speed, efficiency, and scalability. This strategy also ensures you have the best query execution plan when executing your queries under resource constraints.
Generally optimized queries are so important for several reasons. For starters, faster queries mean lower latency and faster response and load time, reflecting your user experience. Optimized queries also mean more effective query processing and resource utilization. Thus, resources are better managed, and more queries can be run more effectively (less memory usage) in the shortest possible time and with fewer resources. This will also lead to cost savings as it delays hardware upgrades and reduces cloud service expenses and system failure.
From a developer’s perspective, optimized SQL queries simplify your work. How? You spend less time on troubleshooting due to less complex queries. This benefits your business by minimizing downtimes. Moreover, these optimized queries are instrumental in ensuring your business meets its SLAs, compliance, and governance standards. For example, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) mandates accurate, timely, and reliable financial data met through optimized queries.

FINAL THOUGHTS ON OPTIMIZING SQL QUERY PERFORMANCE AND FOLLOWING BEST PRACTICES
Optimizing SQL query performance and following best practices starts with choosing which queries to optimize. Once you’ve decided which queries are worth optimizing, you can follow the recommendations above to minimize the number of calculations your software and hardware are responsible for and improve SQL query performance.
When it comes to Microsoft SQL query optimization, SolarWinds Database Performance Analyzer (DPA) and SolarWinds Database Observability (DBO) are two of the best tools on the market. Register for a free, fully functional 14-day trial of Database Performance Analyzer or a 30-day trial for Database Observability.
